
Ansible Vault is a feature that allows users to encrypt values and data structures in Ansible projects. It provides a mechanism to protect sensitive data, such as Passwords or private keys, that is essential for Ansible to run successfully. Ansible automatically decrypts Vault-encrypted content at run time when the key is provided.
There is granularity at the file level with Vault. It either has a fully encrypted or an unencrypted file. It uses the AES256 algorithm to provide symmetric encryption with a user-specified password. As a result, the same password will be used to encrypt and decrypt the content. This is useful in terms of ease of use. Ansible can identify and decrypt vault-encrypted files found while running a playbook or task.
Manage sensitive files with Ansible Vault
The ansible-vault command is the main interface for managing the encrypted content in it. This command is used to first encrypt the file and then view, edit, or decrypt the data.
Creating New Encrypted Files
To create a new Vault encrypted file, use the ansible-vault create command. Then hand over the name of the file to create. For example, to create an encrypted YAML file with the following name Vault.yml for storing sensitive variables.
$ ansible-vault create vault.yml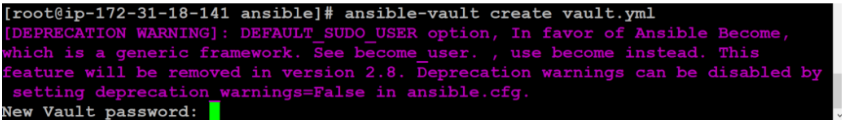
The editor will ask you to confirm your password if you enter it. Write sensitive data to the file by default, the vi/vim editor is present. When you write data and save the file, Ansible encrypts the content when you close the file. If you check the file instead of the word you type, you will see the encrypted block.
$ cat vault.yml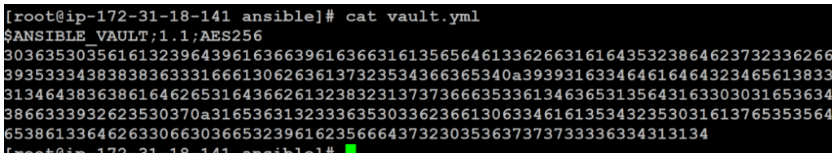
You can see some header information that Ansible uses to know how to handle the file. Followed by the encrypted content indicated by the numbers.
Encrypting Existing Files
If you already have files to encrypt with Vault, use the ansible-vault encryption command instead. If the file does not exist, create a new one as shown below.
$ echo 'this some data ' > newfile.txtYou can now encrypt the existing file by typing:
$ ansible-vault encrypt newfile.txtA new password entry and confirmation screen will appear. Following that, you will receive a message checking the encryption:
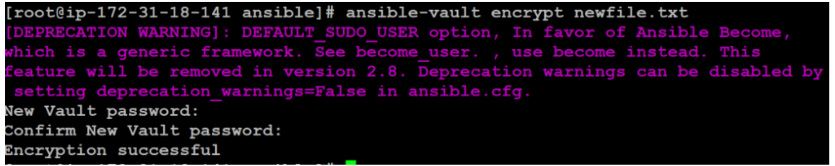
Instead of opening an edit window, ansible-vault encrypts the contents of the file and writes it back to the disk, and replaces the unencrypted version.
If you inspect the file, you will see a similar encrypted pattern:
$ cat newfile.txt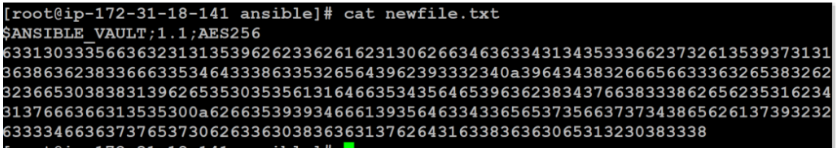
Viewing Encrypted Files
You may need to browse the contents of a Vault-encrypted file without needing to edit or write it to the file system unencrypted. The ansible-vault view command outputs the contents of the file by default. By default, this means that the content will be displayed on your terminal.
Pass the vault encrypted file to the command:
$ ansible-vault view vault.ymlYou will be prompted for the password for the file. If the input is successful, the content will be displayed:
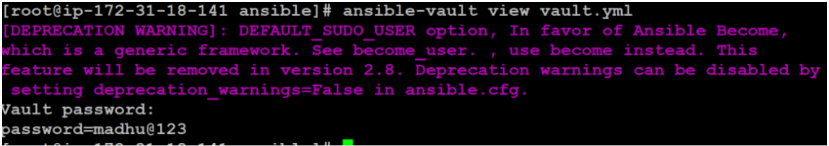
As you can see, the password prompt has been merged into the output of the file contents. Keep it up and be careful when using the ansible-vault view in an automated process.
Editing Encrypted Files
If you need to edit an encrypted file, use the ansible-vault edit command:
$ ansible-vault edit vault.ymlYou will be prompted to enter the password for the file. After typing it, Ansible will open the file in an edit window where you can make the necessary changes.
Once saved, the new content will have the file’s encryption password It will be written to disk.
Manually Decrypting Encrypted Files
To decrypt a file encrypted with Vault, use the ansible-vault decrypt command.
Note:
You should use ansible-vault decrypt only when you want to permanently remove encryption from a file. If you need to view or edit a vault encrypted file, it is usually better to use the ansible-vault view or ansible-vault edit commands, respectively.
Pass the name of the encrypted file:
$ ansible-vault decrypt vault.ymlYou will be prompted to enter the file encryption password. After entering the correct Password then it will decrypts the file:
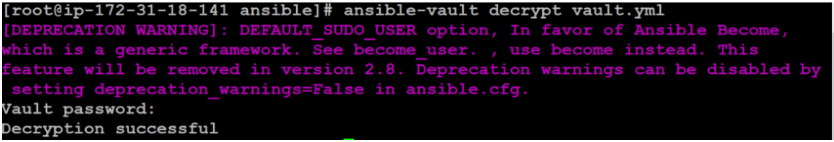
Changing the Password of Encrypted Files
If you need to change the password for the encrypted file, use the ansible-vault rekey command.
$ ansible-vault rekey newfile.txt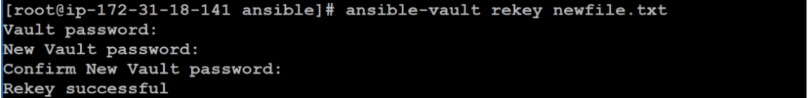
Using an Interactive Prompt
The most straightforward way of decrypting content at runtime is to have Ansible prompt you
for the appropriate credentials. You can do this by adding the –ask-vault-pass to any ansible or
ansible-playbook command. Ansible will prompt you for a password which it will use to try to
decrypt any vault-protected content it finds.
1. First create role under roles folder. For example:
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 ansible]# cd roles/
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 roles]# ansible-galaxy init mail2. After creating role our folder should like below.
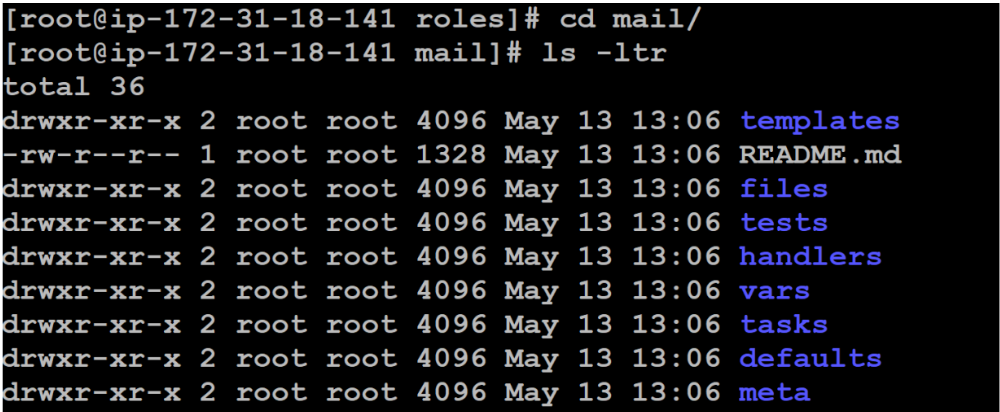
3. Create sensitive data in the var section and it must be a key / value pair like name: madhu
Remember later : must be a space.
4. Then use Ansible Vault encryption to encrypt the data. You will be prompted for a password and confirm the password. You need to remember this password.
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 vars]# ansible-vault encrypt main.yml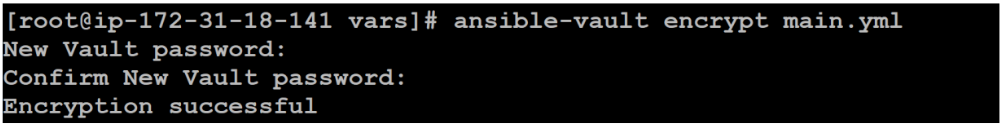
5. Create a playbook based on your requirements. And read the key from sensitive data like {{username}}.
$ cat roles/mail/vars/main.yml
---
# vars file for mail
username: madhu
~After writing sensitive data, you can encrypt it using the ansible-vault encrypt command.
$[root@ip-172-31-18-141 vars]# cat ../tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for mail
- name: get the username
debug:
msg: "myname is {{ username }} "6. Now write the playbook.
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 ansible]# cat vault_example.yml
---
- hosts: nodes
become: yes
gather_facts: False
roles:
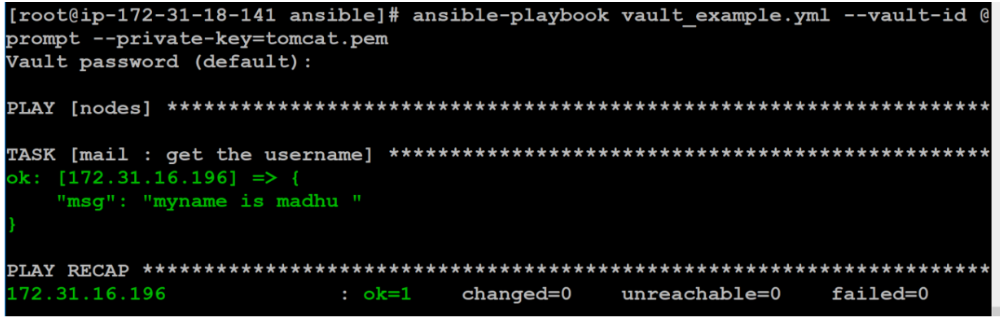
- mail7. Playbooks can be run using –ask-vault-pass or –vault-id @ prompt.
$ ansible-playbook vault_example.yml --vault-id @prompt --private-key=tomcat.pemYou will now be prompted to enter your vault password. Then check the output.
Creating password using api
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 ansible]# openssl passwd -1 -salt testPassword:
Playbook for sending mail after checking version
[root@ip-172-31-18-141 ansible]# cat os_version_check.yml
---
- name: Print linux distribution and version
become: root
hosts: nodes
tasks:
- name: capture output of id command
command: cat /etc/os-release
register: login
- debug:
msg: "{{ login.stdout }}"
- debug:
msg: version comaparision "{{ ansible_distribution_version is version('7.0','>=') }}"
- name: Sending an e-mail using Gmail SMTP servers
mail:
host: smtp.gmail.com
port: 587
secure: starttls
charset: utf-8
sender: ballalallallal
username: ballalallallal
password: ballalallallal
to: ballalallallal
subject: Ansible-report
body: veresion comparision "{{ ansible_distribution_version is version('7', '>=') }}"