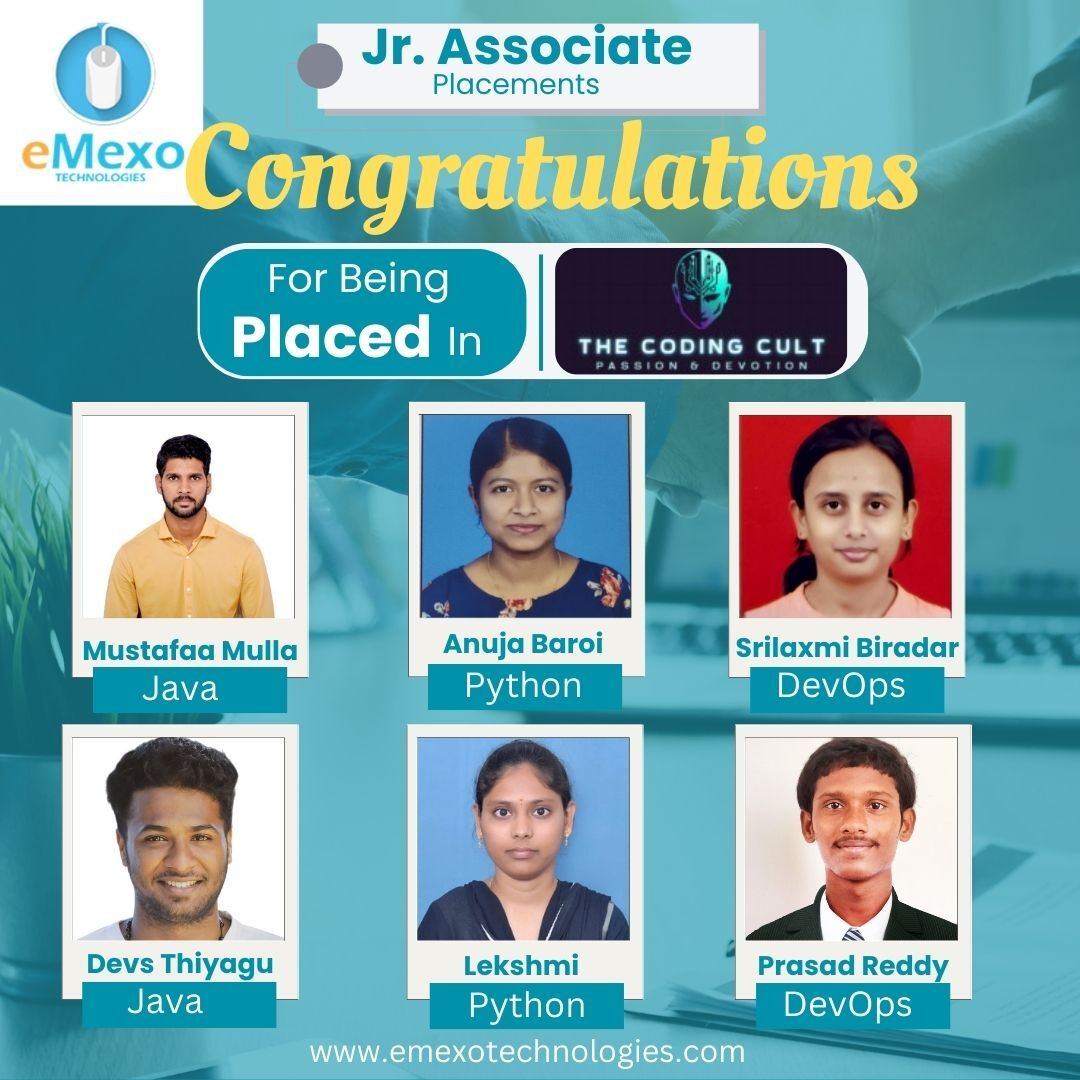
Course Overview
Course Content
- Linear Regression
- Linear Equation
- Slope
- Intercept
- R square value
- Logistic regression
- ODDS ratio
- Probability of success
- Probability of failure Bias Variance Tradeoff
- ROC curve
- Bias Variance Tradeoff
- Hands-on: we’ve reviewed the main ways to approach the problem of modeling data using simple and definite
- K – Nearest Neighbour
- Naïve Bayes Classifier
- Decision Tree – CART
- Decision Tree – C50
- Random Forest
- Hands-on: We have covered the simplest but still very practical machine learning models in an eminently practical way to get us started on the complexity
- Hands-on: where we will cover several regression techniques, it will be time to go and solve a new type of problem that we have not worked on, even if it’s possible to solve the problem with clustering methods (regression), using new mathematical tools for approximating unknown values.
- Hands-on: In it, we will model past data using mathematical functions, and try to model new output based on those modeling.
- CNN – Convolutional Neural Network
- RNN – Recurrent Neural Network
- ANN – Artificial Neural Network
- Hands-on: We took a very important step toward solving complex problems together by means of implementing our first neural
- Hands-on: Now, the following architectures will have familiar elements, and we will be able to extrapolate the knowledge acquired in this chapter, into novel
- Text Classification
- Text Matching
- Levenshtein Distance
- Phonetic Matching
- Flexible String Matching
- Hands-on: provided, you will even be able to create new customized
- Hands-on: As our models won’t be enough to solve very complex problems, in the following chapter, our scope will expand even more, adding the important dimension of time to the set of elements included in our generalization.
- Overview: Visualizations
- Using visualizations
- Create a new report
- Create and arrange visualizations
- Format a visualization
- Create chart visualizations
- Use text, map, and gauge visualizations and save a report
- Use a slicer to filter visualizations
- Sort, copy, and paste visualizations
- Download and use a custom visual from the gallery
- Hands-On
- Modify and Print a Report
- Rename and delete report pages
- Add a filter to a page or report
- Set visualization interactions
- Print a report page
- Send a report to PowerPoint
- Create a Dashboard
- Create and manage dashboards
- Pin a report tile to a dashboard
- Pin a live report page to a dashboard
- Pin a tile from another dashboard
- Pin an Excel element to dashboard
- Manage pinned elements in Excel
- Add a tile to a dashboard
- Build a dashboard with Quick Insights
- Set a Featured (default) dashboard
- Ask Questions about Your Data
- Ask a question with Power BI Q&A
- Tweak your dataset for Q&A
- Enable Cortana for Power BI
- Hands-On
- Use Power BI Mobile Apps
- Get Power BI for mobile
- View reports and dashboards in the iPad app
- Use workspaces in the mobile app
- Sharing from Power BI Mobile
- Use Power BI Desktop
- Install and launch Power BI Desktop
- Get data
- Reduce data
- Transform data
- Relate tables
- Get Power BI Desktop data with the Power BI service
- Export a report from Power BI service to Desktop
- Hands-On
- Area Chart
- Bar Chart
- Box Plot
- Bubble Chart
- Bump Chart
- Bullet Graph
- Circle Views
- Dual Combination Chart
- Dual Lines Chart
- Funnel Chart
- Traditional Funnel Charts
- Gantt Chart
- Grouped Bar or Side by Side Bars Chart
- Heatmap
- Highlight Table
- Histogram
- Cumulative Histogram
- Line Chart
- Lollipop Chart
- Pareto Chart
- Pie Chart
- Scatter Plot
- Stacked Bar Chart
- Text Label
- Tree Map
- Word Cloud
- Waterfall Chart
- Hands-on: Create and use Static Sets
- Hands-on: Create and use Dynamic Sets
- Hands-on: Combine Sets into more Sets
- Hands-on: Use Sets as filters
- Hands-on: Create Sets via Formulas
- Hands-on: Control Sets with Parameters
- Hands-on: Control Reference Lines with Parameters
- Dual Axis Reports
- Blended Axis
- Individual Axis
- Add Reference Lines
- Reference Bands
- Reference Distributions
- Basic Maps
- Symbol Map
- Use Google Maps
- Mapbox Maps as a Background Map
- WMS Server Map as a Background Map
- Hands-on: Create Barcharts
- Hands-on: Create Area Charts
- Hands-on: Create Maps
- Hands-on: Create Interactive Dashboards
- Hands-on: Create Storylines
- Hands-on: Understand Types of Joins and how they work
- Hands-on: Work with Data Blending in Tableau
- Hands-on: Create Table Calculations
- Hands-on: Work with Parameters
- Hands-on: Create Dual Axis Charts
- Hands-on: Create Calculated Fields
- Calculated Fields
- Basic Approach to Calculate Rank
- Advanced Approach to Calculate Ra
- Calculating Running Total
- Filters Introduction
- Quick Filters
- Filters on Dimensions
- Conditional Filters
- Top and Bottom Filters
- Filters on Measures
- Context Filters
- Slicing Filters
- Data Source Filters
- Extract Filters
- Hands-on: Creating Data Extracts in Tableau
- Hands-on: Understand Aggregation, Granularity, and Level of Detail
- Hands-on: Adding Filters and Quick Filters
- Excel tutorial
- Text to Columns
- Concatenate
- The Concatenate Function
- The Right Function with Concatenation
- Absolute Cell References
- Data Validation
- Time and Date Calculations
- Conditional Formatting
- Exploring Styles and Clearing Formatting
- Using Conditional Formatting to Hide Cells
- Using the IF Function
- Changing the “Value if false” Condition to Text
- Pivot Tables
- Creating a Pivot Table
- Specifying PivotTable Data
- Changing a PivotTables Calculation
- Filtering and Sorting a PivotTable
- Creating a PivotChart
- Grouping Items
- Updating a PivotTable
- Formatting a PivotTable
- Using Slicers
- Charts
- Creating a Simple Chart
- Charting Non-Adjacent Cells
- Creating a Chart Using the Chart Wizard
- Modifying Charts
- Moving an Embedded Chart
- Sizing an Embedded Chart
- Changing the Chart Type
- Chart Types
- Changing the Way Data is Displayed
- Moving the Legend
- Formatting Charts
- Adding Chart Items
- Formatting All Text
- Formatting and Aligning Numbers
- Formatting the Plot Area
- Formatting Data Markers
- Pie Charts
- Creating a Pie Chart
- Moving the Pie Chart to its Own Sheet
- Adding Data Labels
- Exploding a Slice of a Pie Chart
- Data Analysis − Overview
- types of Data Analysis
- Data Analysis Process
- Working with Range Names
- Copying Name using Formula Autocomplete
- Range Name Syntax Rules
- Creating Range Names
- Creating Names for Constants
- Managing Names
- Scope of a Name
- Editing Names
- Applying Names
- Using Names in a Formula
- Viewing Names in a Workbook
- Copying Formulas with Names
- Difference between Tables and Ranges
- Create Table
- Table Name
- Managing Names in a Table
- Table Headers replacing Column Letters
- Propagation of a Formula in a Table
- Resize Table
- Remove Duplicates
- Convert to Range
- Table Style Options
- Table Styles
- Cleaning Data with Text Functions
- Removing Unwanted Characters from Text
- Extracting Data Values from Text
- Formatting Data with Text Functions
- Date Formats
- Conditional Formatting
- Sorting
- Filtering
- Lookup Functions
- Pivoting
- Hands-On
- Introduction to Probability
- Probability Addition Rule
- Probability Multiplication Rule
- Distributions
- Correlation
- Regression
- Hypothesis Testing
- ANOVA and Chi-Square Tests
- Data Cleaning
- Imputation Techniques
- Measure Of central tendency, Measures of Dispersion
- Graphical Techniques, Skewness & Kurtosis, Box Plot
- Descriptive Stats
- Central Limit Theorem, Confidence interval
- Hands-On
- Fundamentals of SQL Syntax and Statements
- Data Filtering and Sorting Techniques
- Utilization of Single-Row Functions
- Aggregate and Group Functions
- Analytical (Window) Functions
- Data Definition Language (DDL) – Creating and Managing Schema Objects
- Data Manipulation Language (DML) – Inserting, Updating, and Deleting Data
- Implementation of Data Constraints
- Set Operations – UNION, INTERSECT, and MINUS
- Subqueries and Nested Queries
- Joins and Multi-Table Queries
- Transaction Control Language (TCL) – COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT
- Data Control Language (DCL) – GRANT and REVOKE Permission